Covalent Bond (Regular and Reversible)
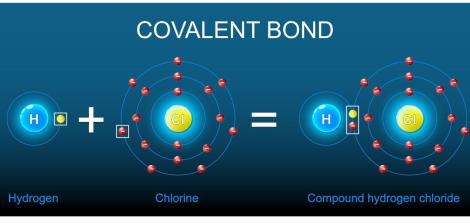
A covalent bond is a strong connection between two atoms in which they share electrons. This sharing helps each atom complete its outermost electron shell and become more stable. Covalent bonds form the basis of all molecules and occur mainly between non-metal atoms.
What force holds the atoms together?
The main force is the electrical attraction between the positively charged nuclei of the two atoms and the shared pair of electrons between them. This shared pair is what connects the atoms and forms the molecule.
What types of covalent bonds exist?
Covalent bonds differ in the number of shared electrons (single, double, or triple bonds) and in their polarity (a nonpolar bond with equal sharing of electrons, or a polar bond in which one atom pulls more strongly).
What is a reversible covalent bond, and why is it important in drug development?
A regular covalent bond is considered strong and permanent. A reversible covalent bond, however, can break and reform relatively easily in response to a stimulus. Reversible binding of drugs to their target site allows for high efficacy while reducing toxic side effects.
How is a covalent bond different from an ionic bond?
A covalent bond is based on the sharing of electrons. In contrast, an ionic bond is based on the complete transfer of an electron from one atom to another, creating ions that are strongly attracted to each other by electrical forces.
Last Updated Date : 31/12/2025