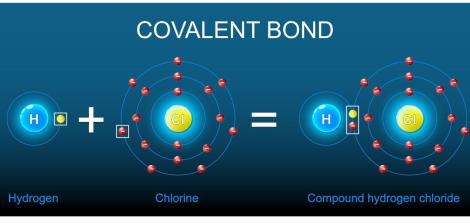
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process in which genetic information(the instructions encoded within a DNA molecule) is translated into concrete action within the cell. In most cases, the result is the production of a protein- a molecule that actively functions and influences the cell’s structure, function and responses.
Every cell in the body contains the same genes, but only some of them are active at any given moment. The cell “chooses” which genes to express based on its type, its stage of development, environmental conditions, and the needs of the body.
The stages of the process include transcription, in which the selected gene is “copied” into an information unit called mRNA (short for messenger RNA), and translation, in which the mRNA molecule exits the nucleus and moves into the cell’s activity zone (the cytoplasm), where cellular structures called ribosomes read the instructions and construct the corresponding protein accordingly.
There are also genes that do not lead to the production of a protein but are expressed through the creation of other RNA molecules that serve essential functions on their own.
Malfunctions in gene expression- such as the activation of a gene in the wrong place or at the wrong time- can lead to diseases like cancer and diabetes, hereditary disorders or neurological conditions.
Therefore, the study of gene expression is a key field in medicine and biology and serves as a foundation for the development of advanced diagnostics and personalized treatments.
More on gene expression in an interview with Prof. Yaron Shav-Tal on the Dangoor website >>
Last Updated Date : 31/07/2025