Neurodegenerative Diseases

Neurodegenerative diseases are disorders of the nervous system characterized by the gradual death of nerve cells, leading to a continuous decline in brain and nervous system function. In most cases, these diseases cannot be fully cured and tend to worsen over time.
What causes neurodegenerative diseases?
Several factors can contribute to their development, including the buildup of defective proteins inside cells, chronic inflammation in the brain, oxidative damage to nerve cells, genetic mutations, exposure to toxins, and other underlying conditions.
What are the main neurodegenerative diseases and their symptoms?
Alzheimer’s disease – the most common neurodegenerative disorder, affecting memory and thinking abilities. Parkinson’s disease – impairs movement, causing tremors and muscle stiffness. Huntington’s disease – a hereditary disorder leading to involuntary movements and emotional changes. ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) and SMA (Spinal Muscular Atrophy) – damage motor neurons, resulting in progressive muscle weakness.
What increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases?
Advanced age is the most significant risk factor, but others include genetic predisposition, exposure to environmental toxins, repeated head injuries, smoking, lack of physical activity, social isolation, and chronic illnesses such as diabetes and heart disease.
How are neurodegenerative diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive neurological examination, cognitive testing, brain imaging, blood tests to rule out other causes, and sometimes genetic testing or analysis of specific proteins in cerebrospinal fluid.
Is there a cure or a way to prevent these diseases?
Currently, there is no cure for neurodegenerative diseases. Available treatments focus on alleviating symptoms and slowing disease progression. Research supports a multidisciplinary approach that combines physical activity, healthy nutrition, cognitive training, and proper sleep hygiene as key components of both prevention and management.
Why is early diagnosis important?
Early detection allows treatment to begin sooner, helps patients and families plan ahead, improves quality of life, and enables participation in clinical trials that may offer promising new therapies.
What promising developments are emerging in research?
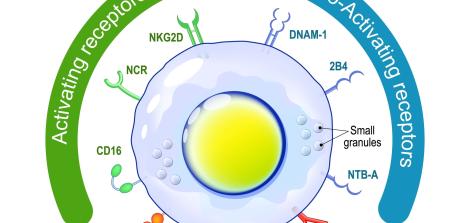
Current research focuses on early detection through biological markers, drugs that clear damaged proteins from the brain, stem cell therapy, and genetic treatments. At the Dangoor Center for Personalized Medicine, scientists are exploring innovative immunotherapy strategies that may one day lead to effective treatments for these debilitating diseases.
Last Updated Date : 05/11/2025