Microbiota
The name Microbiota refers to an ecological population of microorganisms, mostly bacteria, that develop inside and on the living body, mostly in the digestive system, with which they interact in a symbiotic process.
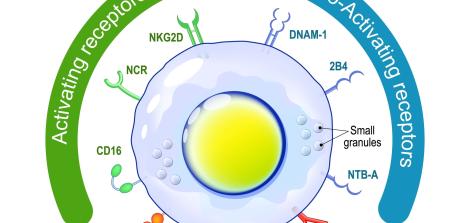
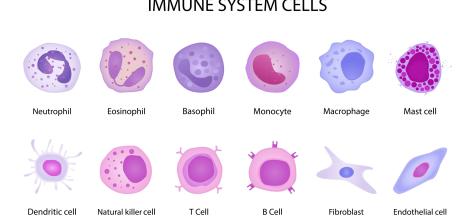
The microbiota in the digestive system is the largest and most commonly researched population, and includes bacteria, viruses, fungi and single-celled organisms that interact with the hosting body in different ways. Studies show that the microbiota maintains bilateral biochemical communication with the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord – and plays an important role in maintaining the body’s proper functions and in particular some immune system processes. Bilateral communication with the nervous system and the brain forms the basis for microbiota research conducted at the Dangoor Center for Personalized Medicine, which is intended to help find treatments for autoimmune diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, fibromyalgia and, apparently, cancer.
Last Updated Date : 22/08/2024